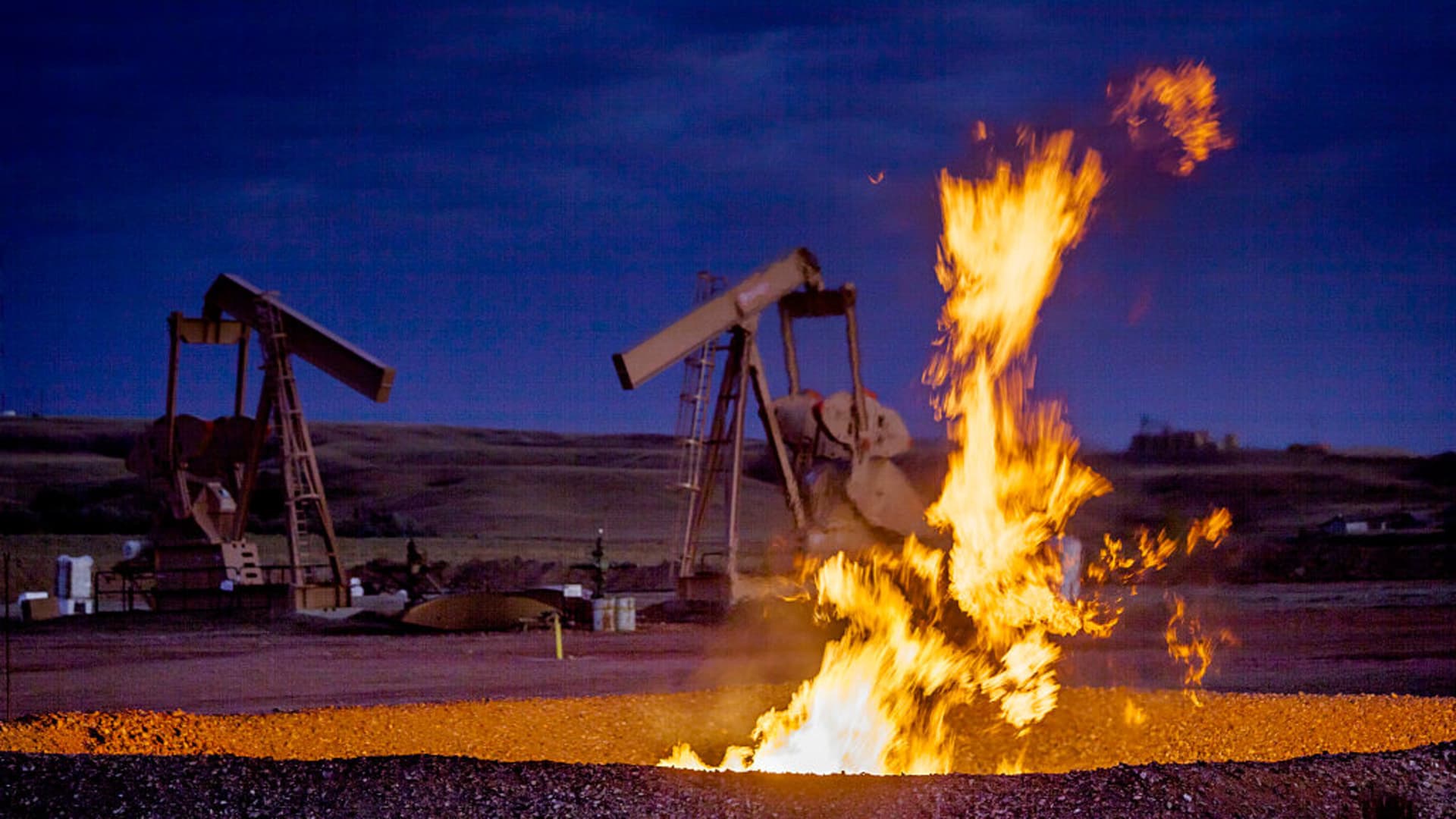
Flames from a flaring pit in the vicinity of a very well in the Bakken Oil Area. The primary component of all-natural gas is methane, which is odorless when it comes specifically out of the gas nicely. In addition to methane, purely natural gasoline ordinarily contains other hydrocarbons this kind of as ethane, propane, butane, and pentanes.
Orjan F. Ellingvag | Corbis News | Getty Illustrations or photos
The intensity of methane and greenhouse gasoline emissions from the oil and gasoline sector declined 28% and 30%, respectively, involving 2019 and 2021 amid the premier producers in the nation, despite an increase in pure gasoline creation, according to an analysis released by the nonprofits Cleanse Air Job Force and Ceres.
The report, which assessed the creation-based mostly emissions of extra than 300 U.S. producers, located that the methane emissions intensity of pure gas creation and the greenhouse gasoline emissions intensity of oil and fuel creation change significantly across providers.
Pure gasoline producers in the maximum quartile of methane emissions intensity have an typical emissions intensity which is nearly 26 moments higher than producers in the least expensive quartile, the review identified. And oil and gas producers in the best quartile of greenhouse fuel emissions depth have an normal emissions intensity that is extra than 13 times increased than producers in the least expensive quartile.
“Oil and fuel producers are not equals when it will come to methane emissions, and this research helps make very clear that a firm’s climate effect is a direct end result of operational and financial commitment selections within its management,” Andrew Logan, senior director of oil and gasoline at Ceres, mentioned in a assertion.
Greenhouse gasoline emissions from the U.S. oil and gas sector come generally from the extraction and output procedure, wherever methane and other world-warming gases are released by venting, flaring and leaks.
The decline in noted methane emissions involving 2019 and 2021 was driven by a reduction of described emissions from pneumatic controllers, whilst involved fuel venting and flaring have been liable for the greatest minimize in noted carbon dioxide emissions, the report stated.
Pneumatic controllers, devices that use compressed air to control pressures or temperature in the creation process, have been the major supply of complete reported methane emissions, creating up 67% of emissions, the examine uncovered.
Methane is about 84 situations additional strong than carbon dioxide when it arrives to warming the environment, but does not final as lengthy in the atmosphere in advance of it breaks down. Scientists have warned that methane emissions must be drastically reduced to steer clear of the worst impacts of local weather modify.
The examine was made to offer an analysis of greenhouse fuel emission details that corporations are disclosing to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
The authors observed that the trends in emissions are not constant across basins or unique organizations and can fluctuate year to yr. They also claimed the report isn’t going to account for unreported emissions that arrive from significant leaks and emissions from scaled-down producers.
Lesley Feldman, investigate and examination manager at the Clean up Air Process Pressure, said the results underscore the have to have for powerful federal and condition polices that can standardize finest tactics throughout the sector.
Methane emissions by itself are dependable for roughly fifty percent a degree Celsius of worldwide warming to day, and methane degrees in the atmosphere go on to increase every yr, in accordance to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.