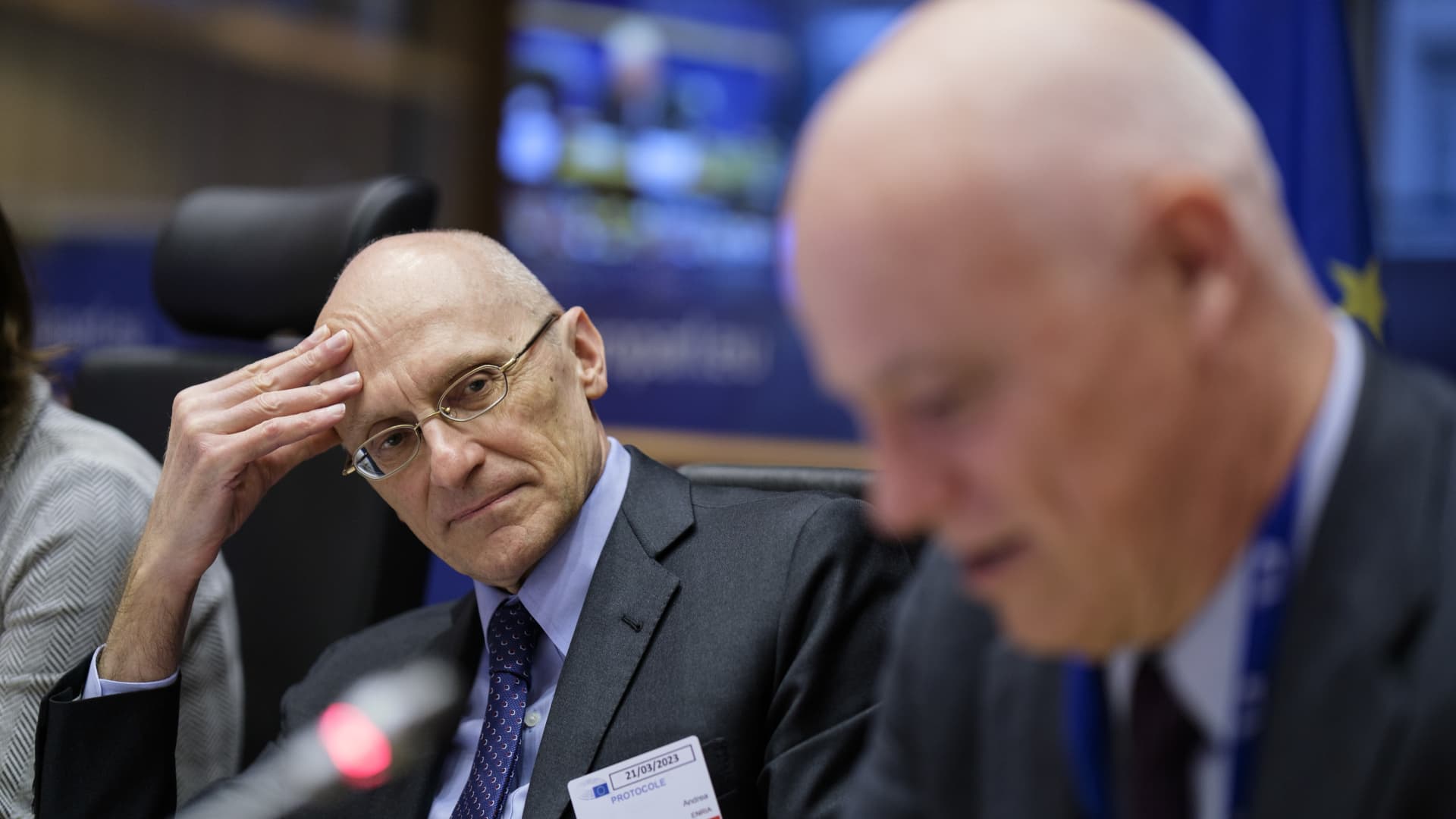

Chair of the ECB Supervisory Board Andrea Enria and Chairperson of the European Banking Authority (EBA) Jose Manuel Campa in the European Parliament on March 21, 2023.
Thierry Monasse | Getty Photographs Information | Getty Visuals
U.S. regulators produced problems in failing to stop the collapse of Silicon Valley Financial institution and other monetary institutions, according to lawmakers in the European Union who believe that this is also a minute for some self-assessment in Europe.
Silvergate Money, a bank centered on cryptocurrency, was the very first to fall, expressing March 8 that it would be ceasing functions. Soon following, Silicon Valley Bank failed following a run on deposits. Signature Lender, which targeted on lending to true estate corporations, then noticed deposit outflows foremost regulators to seize the lender to avert contagion across the sector.
Given that then, 1st Republic Lender has also obtained assistance from other banking companies amid fears of a wider shock to the money system. And in Switzerland, a non-member of the European Union, authorities experienced to rescue Credit rating Suisse by inquiring UBS to step in with an acquisition.
In the meantime, regulators and officials throughout the European Union have been anxious about possible contagion to their have banking sector. Following all, it can be not been that very long due to the fact European banking institutions were in the depths of the international monetary disaster.
“There is no immediate study across of U.S. activities to [the] euro place significant financial institutions,” Andrea Enria, chair of the European Central Bank’s supervisory board, stated Tuesday. Like him, an array of officers have designed an energy to anxiety that the European banking method is in considerably better share when compared to 2008.
The U.S. lacks some controls.
Paul Tang
Lawmaker in the European Parliament
This reinforces the view in the EU that the U.S. should really discover from some of the regulatory operates set in position in the euro region since the economical crisis.
“You will need more robust regulation … in that sense the U.S. lacks some controls,” Paul Tang, a lawmaker and a member of the European Parliament’s economic committee, advised CNBC.
When requested if U.S. regulators produced some issues, hence failing to protect against the modern banking turmoil, he mentioned: “I surely imagine so, you need to have to have scrutiny. That was the concept from 2008.”
In the heart of European policymaking, in Brussels, an formal, who did not want to be named due to the politically delicate nature of the subject, instructed CNBC that numerous meetings among EU officials in the latest times “pressured the failures of regulation [in the U.S.] significantly when when compared with the EU.”
One particular of the crucial distinctions is that the U.S. has a extra calm set of funds procedures for lesser banks.
“The most important change is the Basel III specifications,” Stéphanie Yon-Courtin, a member of the European Parliament explained to CNBC. “These banking guidelines,” she claimed, “implement to quite couple banking companies — this is the place the difficulty lays.”
Basel III is a set of reforms that strengthens the supervision and danger management of banks and has been created considering that 2008.
It applies to most European financial institutions, but American creditors with a harmony sheet underneath $250 billion do not have to comply with them.
‘Remain vigilant’
Irrespective of some of the criticism towards American regulators, the EU acknowledges this is not the time to be complacent. “We have to keep on being vigilant,” Yon-Courtin reported. “We have to be thorough and be certain these guidelines are continue to suit for objective,” she included, pushing for a consistent monitoring of the rulebook.
1 of the major discussions in the EU in recent days has actually been the have to have to strengthen the European Banking Union — a set of legislation introduced in 2014 to make European banking companies far more robust.
The debate has been politically sensitive, but the reality that large interest premiums are below to continue to be has made it even additional significant.
“We are perfectly mindful that the ongoing quick tempo normalization of monetary policy problems is expanding our banks’ exposure to fascination level possibility,” Enria, the chair of the ECB’s supervisory board, mentioned Tuesday.







