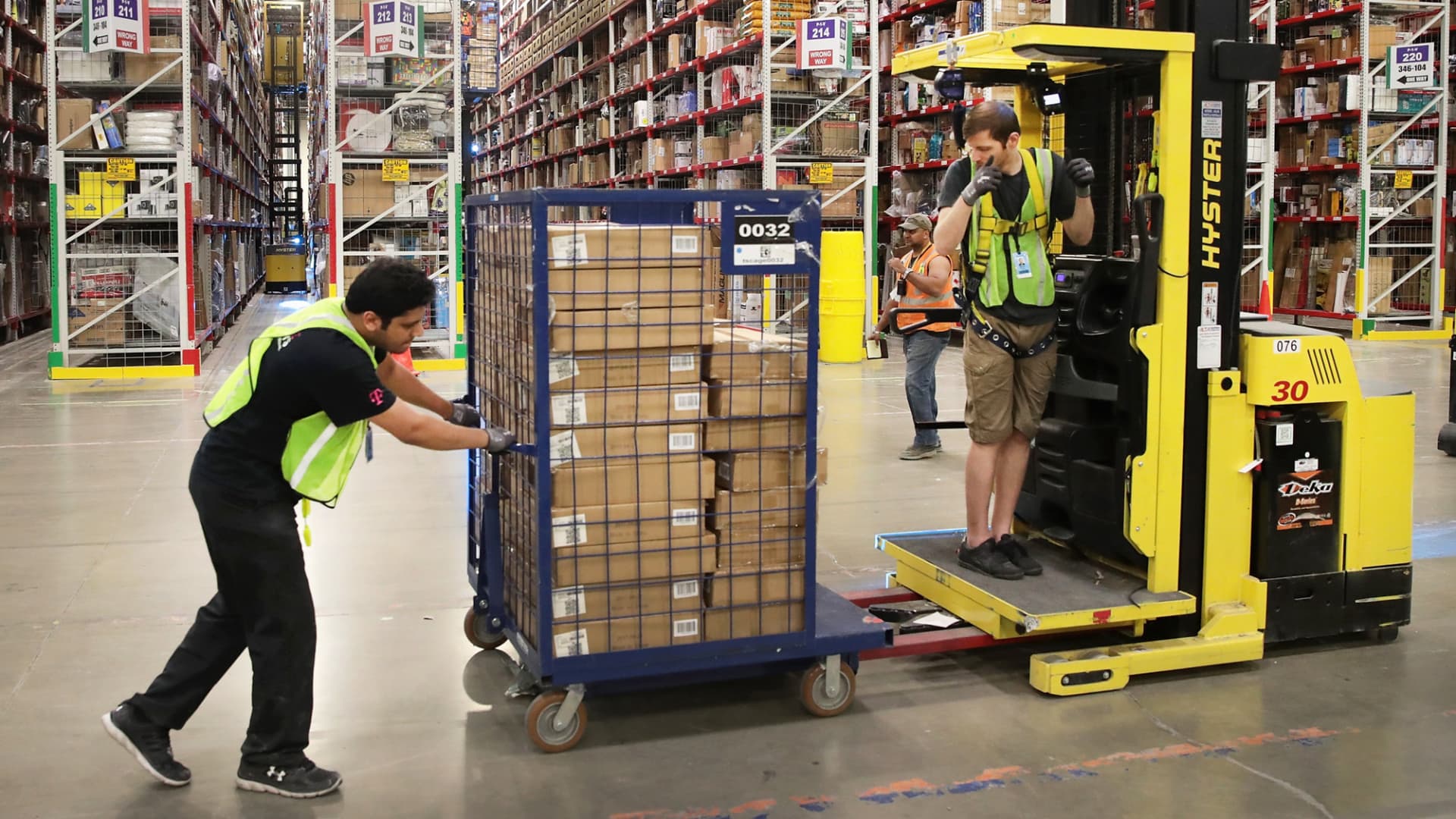
Democratic Sen. Ed Markey, D-Mass., on Thursday released new legislation to regulate the use of efficiency quotas by warehouse businesses these types of as Amazon, a tool critics have explained encourages personnel to get the job done more rapidly and devoid of recurrent breaks, placing them at better chance of injuries.
The invoice, known as the Warehouse Employee Defense Act, is the very first attempt to police warehouse quotas at the federal degree. It will come after identical rules have passed in various states, which include California, New York, Washington and Minnesota.
The legislation would require employers to be far more clear about office quotas and possible disciplinary outcomes. Employers would also have to have to deliver workers with at minimum two business days’ observe of any variations to quotas or office surveillance.
It also seeks to ban organizations from employing “dangerous quotas” like “time off task,” an oft-scrutinized metric utilized by Amazon to evaluate the time a worker isn’t really scanning products while on the clock. Staff have argued the time off endeavor plan can make working ailments much more strenuous and that it really is used as a software to surveil personnel.
“Amazon has perfected a punishing quota technique that pushes employees to and past their physical boundaries,” Markey, a member of the Wellness, Education and learning, Labor and Pensions Committee’s Subcommittee on Employment and Workplace Security, claimed at a press meeting saying the bill.
“They set prerequisites for how quite a few packages personnel have to scan without telling workers what these requirements are. Then they fireplace workers who fall short to gain their unattainable recreation,” Markey included.
Amazon’s use of quotas in its warehouse and shipping functions has been a recurrent matter of debate along with broader scrutiny of the basic safety of its frontline employees. The enterprise — the next-premier private employer in the U.S. — has earlier explained it would not use set quotas. Instead, the organization reported, it depends on “general performance anticipations” that aspect in multiple indicators, these kinds of as how specific groups at a web-site are performing. It really is also disputed allegations that staff do not get more than enough breaks.
Amazon has a “time logged in” policy that “assesses no matter whether workforce are essentially doing the job when they’re logged in at their station,” Amazon spokesperson Steve Kelly explained. Kelly added that staff can look at their functionality whenever and that administrators offer coaching to having difficulties personnel.
Still some Amazon warehouse staff say the company’s productivity quotas are opaque and typically determined by algorithms, and that they facial area disciplinary action or termination for failing to meet them. The Occupational Basic safety and Overall health Administration final yr issued citations in opposition to Amazon for exposing staff members to security hazards, and pointed to its tempo of operate as a driving aspect.
OSHA and the U.S. Attorney’s Office are investigating conditions at numerous warehouses, though the U.S. Department of Justice is analyzing no matter if Amazon underreports accidents. Amazon has explained it disagrees with the DOJ and OSHA’s allegations.
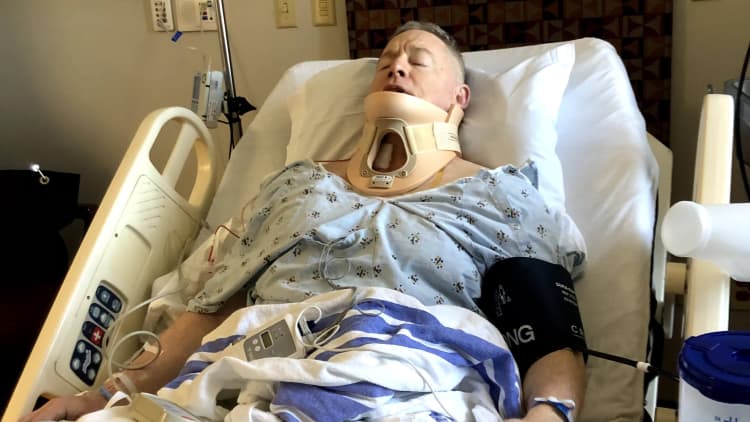
Wendy Taylor, a packer at an Amazon warehouse in Missouri, stated through Markey’s push conference on Thursday that she and other folks are “preventing for quota transparency.” Taylor claimed final March she “tripped and fell flat on my encounter” about a pallet, but was requested back again to operate by onsite health care employees. Her medical professional later discovered she’d torn her meniscus throughout the drop.
Taylor blamed Amazon’s “inhumane work premiums” for the injuries, and extra, “Amazon personnel supply exact same-day delivery, but we can’t even get the exact same-working day care we deserve.”
Enjoy: Amazon’s worker basic safety dangers occur under fireplace from regulators and the DOJ