A multi-calendar year investigation into the safety of Tesla’s driver guidance units by the Nationwide Highway Traffic Security Administration, or NHTSA, is drawing around a close.
Reuters’ David Shepardson first reported on the hottest developments Thursday, citing NHTSA performing administrator Ann Carlson. CNBC confirmed the report with the federal car or truck security regulators.
A spokesperson for NHTSA declined to disclose additional information, but explained to CNBC in an e-mail, “We affirm the reviews to Reuters,” and “NHTSA’s Tesla investigations remain open, and the agency typically does not remark on open up investigations.”
The company initiated a security probe of Tesla’s driver assistance programs — now marketed in the U.S. as Autopilot, Full Self-Driving and FSD Beta alternatives — in 2021 immediately after it recognized a string of crashes in which Tesla drivers, assumed to be applying the company’s driver assistance systems, crashed into to start with responders’ stationary autos.
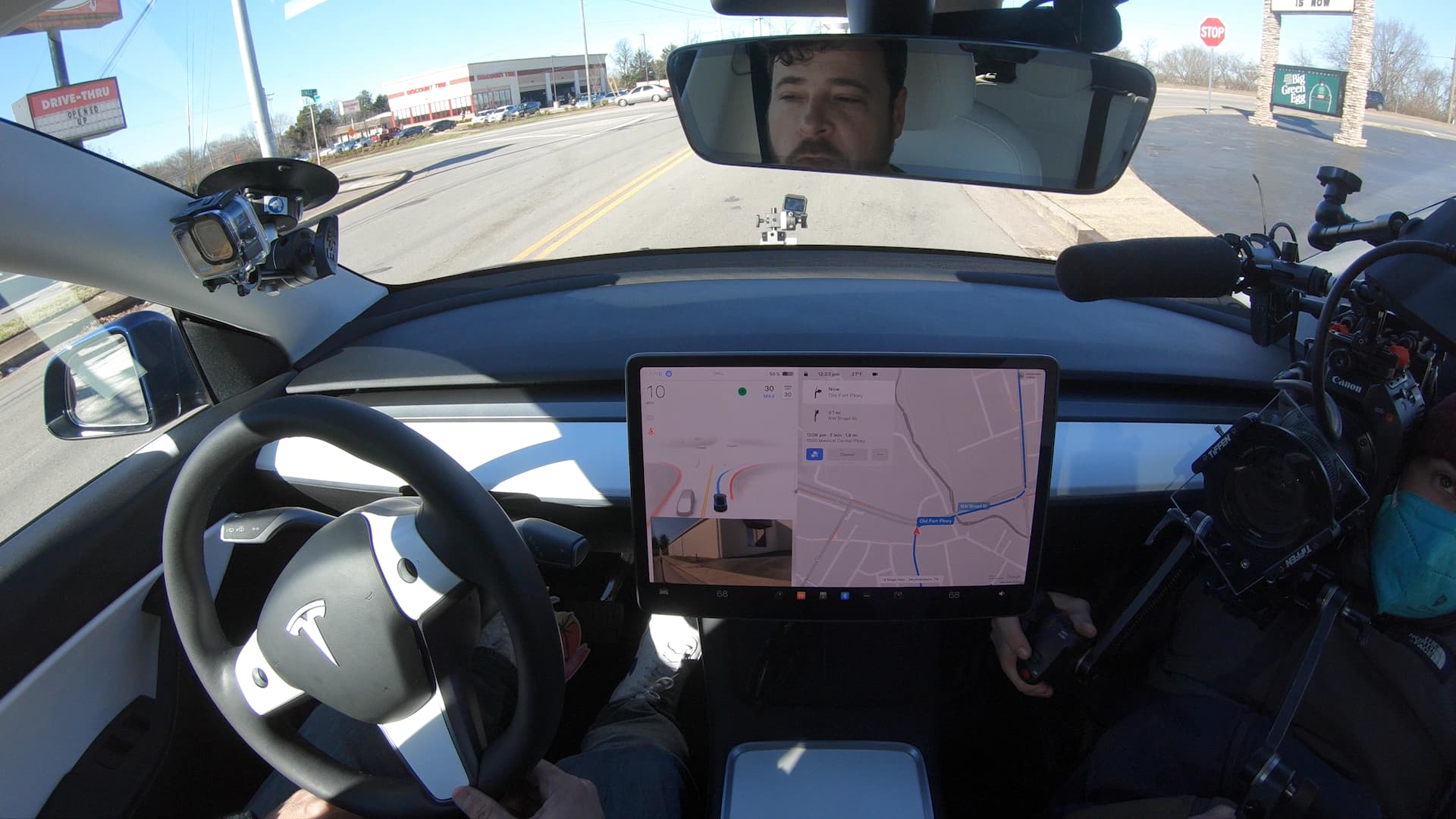
Even with their names, none of Tesla’s driver assistance options make their cars autonomous. Tesla automobiles are unable to purpose as robotaxis like people operated by GM-owned Cruise or Alphabet‘s Waymo. Rather, Tesla motor vehicles call for a human driver at the wheel, all set to steer or brake at any time. Tesla’s conventional Autopilot and top quality Total Self-Driving systems only command braking, steering and acceleration in constrained instances.
Tesla CEO Elon Musk — who also owns and runs the social community X (formerly Twitter) — normally implies Tesla cars are autonomous. For illustration, on July 23, an ex-Tesla staff who led the company’s AI computer software engineering posted on the social network about ChatGPT, and how substantially that generative AI device amazed his dad and mom when he confirmed it to them for the initial time. Musk responded: “Same occurs with Tesla FSD. I forget about that most people today on Earth have no thought vehicles can travel them selves.”
In its owners’ manuals, Tesla tells drivers who use Autopilot or FSD: “Continue to keep your hands on the steering wheel at all occasions and be conscious of highway disorders, bordering website traffic, and other road consumers (these kinds of as pedestrians and cyclists). Always be well prepared to consider immediate action. Failure to observe these recommendations could bring about injury, critical injury or demise.”
The company’s autos function a driver checking method which employs in-cabin cameras and sensors in the steering wheel to detect no matter whether a driver is spending adequate interest to the road and driving job. The program will “nag” motorists with a chime and message on the car’s touchscreen to pay out attention and set their hands on the wheel. But it can be not very clear that this is a sturdy ample program to guarantee harmless use of Tesla’s driver guidance attributes.
Tesla has previously conducted voluntary recalls of its autos thanks to other complications with Autopilot and FSD Beta and promised to produce more than-the-air software program updates that would cure the challenges. But in July, the company expected Elon Musk’s automaker to send out more comprehensive info on the functionality of their driver guidance programs to assess as aspect of its Autopilot security investigations.
NHTSA publishes information regularly on vehicle crashes in the U.S. that included innovative driver support systems like Tesla Autopilot, Full Self Driving or FSD Beta, dubbed “level 2” below industry specifications from SAE Global.
The hottest facts from that Standing Standard Get crash report states there have been at the very least 26 incidents involving Tesla automobiles equipped with amount 2 units ensuing in fatalities from August 1, 2019 by means of mid-July this yr. In 23 of these incidents, the agency report suggests, Tesla’s driver support characteristics ended up in use within 30 seconds of the collision. In three incidents, it is really not known no matter if these capabilities ended up applied.
Ford is the only other automaker reporting a fatal collision that included 1 of its autos equipped with stage 2 driver guidance. It was not recognized if the procedure was engaged previous that crash, in accordance to the NHTSA SGO report.
Tesla did not answer to a request for remark.






