
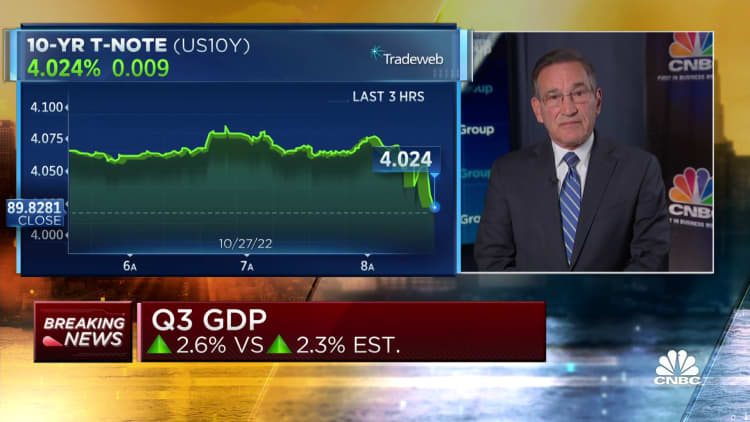
The U.S. financial system posted its 1st period of time of constructive development for 2022 in the 3rd quarter, at minimum temporarily easing recession fears, the Bureau of Economic Examination reported Thursday.
GDP, a sum of all the products and services generated from July by means of September, improved at a 2.6% annualized pace for the interval, in accordance to the advance estimate. That was earlier mentioned in opposition to the Dow Jones forecast for 2.3%.
That reading through follows consecutive unfavorable quarters to start out the yr, meeting a commonly accepted definition of economic downturn, though the Nationwide Bureau of Financial Research is usually deemed the arbiter of downturns and expansions.
The progress came in large section owing to a narrowing trade deficit, which economists anticipated and look at to be a a single-off prevalence that would not be recurring in foreseeable future quarters.
GDP gains also came from raises in shopper spending, nonresidential fastened investment and government paying. The report mirrored an ongoing change to companies shelling out over goods, with paying on the previous raising 2.8% while merchandise spending dropped 1.2%.
Declines in household fastened financial commitment and non-public inventories offset the gains, the BEA said.
“Total, though the 2.6% rebound in the 3rd quarter additional than reversed the decrease in the first fifty percent of the yr, we you should not anticipate this toughness to be sustained,” wrote Paul Ashworth, main North The usa economist at Capital Economics. “Exports will quickly fade and domestic desire is finding crushed underneath the excess weight of larger desire rates. We assume the overall economy to enter a mild economic downturn in the initially 50 % of upcoming year.”
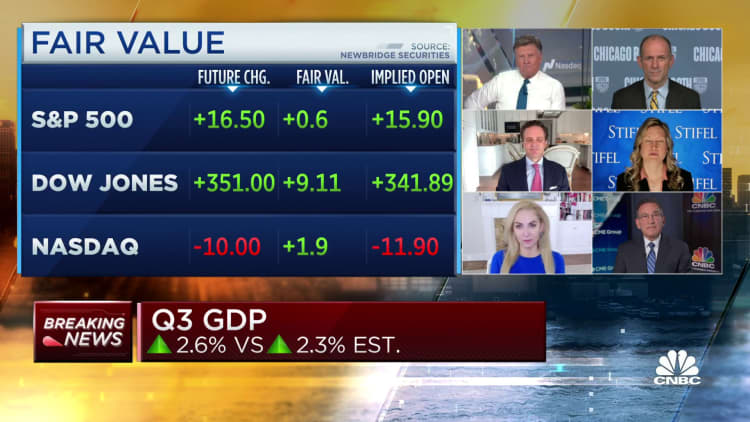
Marketplaces had been better following the release, with the Dow Jones Industrial Average getting a lot more than 300 details in early trading on Wall Avenue.
In other economic news Thursday, weekly jobless statements edged bigger to 217,000 but have been continue to below the 220,000 estimate. Also, orders for prolonged-lasting products enhanced .4% in September from the earlier thirty day period, underneath the .7% expectation.
The report arrives as policymakers struggle a pitched struggle in opposition to inflation, which is jogging around its best concentrations in a lot more than 40 a long time. Value surges have occur thanks a variety of factors, quite a few relevant to the Covid pandemic but also pushed by unparalleled fiscal and financial stimulus that is even now working its way as a result of the economic program.
The fundamental photograph from the BEA report showed an overall economy slowing in critical locations, notably the client and personal financial commitment.
Shopper paying as calculated as a result of own intake expenditures improved at just a 1.4% speed in the quarter, down from 2% in Q2. Gross non-public domestic financial investment fell 8.5%, continuing a development after falling 14.1% in the 2nd quarter. Residential expenditure, a gauge of homebuilding, tumbled 26.4% right after slipping 17.8% in Q2, reflecting a sharp slowdown in the true estate industry.
On the moreover aspect, exports, which incorporate to GDP, rose 14.4% whilst imports, which subtract, dropped 6.9%. Net exports of merchandise and expert services added 2.77 proportion details to the headline full, meaning GDP in essence would have been flat otherwise.
There was some good news on the inflation front.
The chain-weighted rate index, a value-of-living measure that adjusts for shopper actions, rose 4.1% for the quarter, perfectly underneath the Dow Jones estimate for a 5.3% achieve, because of in big aspect to falling strength prices. Also, the private consumption expenses rate index, a vital inflation measure for the Federal Reserve, increased 4.2%, down sharply from 7.3% in the prior quarter. Main charges, excluding food and electrical power, improved 4.5%, about in line with Wall Street expectations.
Before this calendar year, the Fed commenced a campaign of fascination level hikes aimed at taming inflation. Given that March, the central financial institution has lifted its benchmark borrowing level by 3 proportion factors, getting it to its greatest level considering the fact that just just before the worst of the economical disaster.
These raises are aimed at slowing the move of income by the financial system and taming a work market where openings outnumber available employees by just about 2 to 1, a problem that has driven up wages and contributed to a wage-selling price spiral that economists concern will suggestion the U.S. into recession.
“Our worries about likely into economic downturn would not essentially be from any of this info. It comes extra from how considerably the Fed cranks up rates and what takes place when companies and buyers react to this,” stated Luke Tilley, main economist at Wilmington Have faith in.
“The most encouraging issue is you nevertheless have buyer paying out, you however have occupation progress and wage expansion and that ought to aid on the purchaser shelling out facet,” he additional. “What we would be most worried about would be a sharp pullback by businesses in their choosing.”
The Fed is broadly acknowledged to approve a fourth consecutive .75 share point interest level hike at its assembly upcoming week, but then may possibly gradual the pace of raises afterward as officers just take time to evaluate the affect of plan on economic ailments.
Policymakers will get yet another, more existing glimpse at inflation data when the BEA releases a report Friday that will involve own intake expenses selling prices for September. That evaluate is expected to demonstrate that main selling prices excluding foodstuff and strength rose 5.2% from a yr ago and .5% on a month to month foundation.






